Types, How They Work, and Their Role in the Future: Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Nov 26, 2025
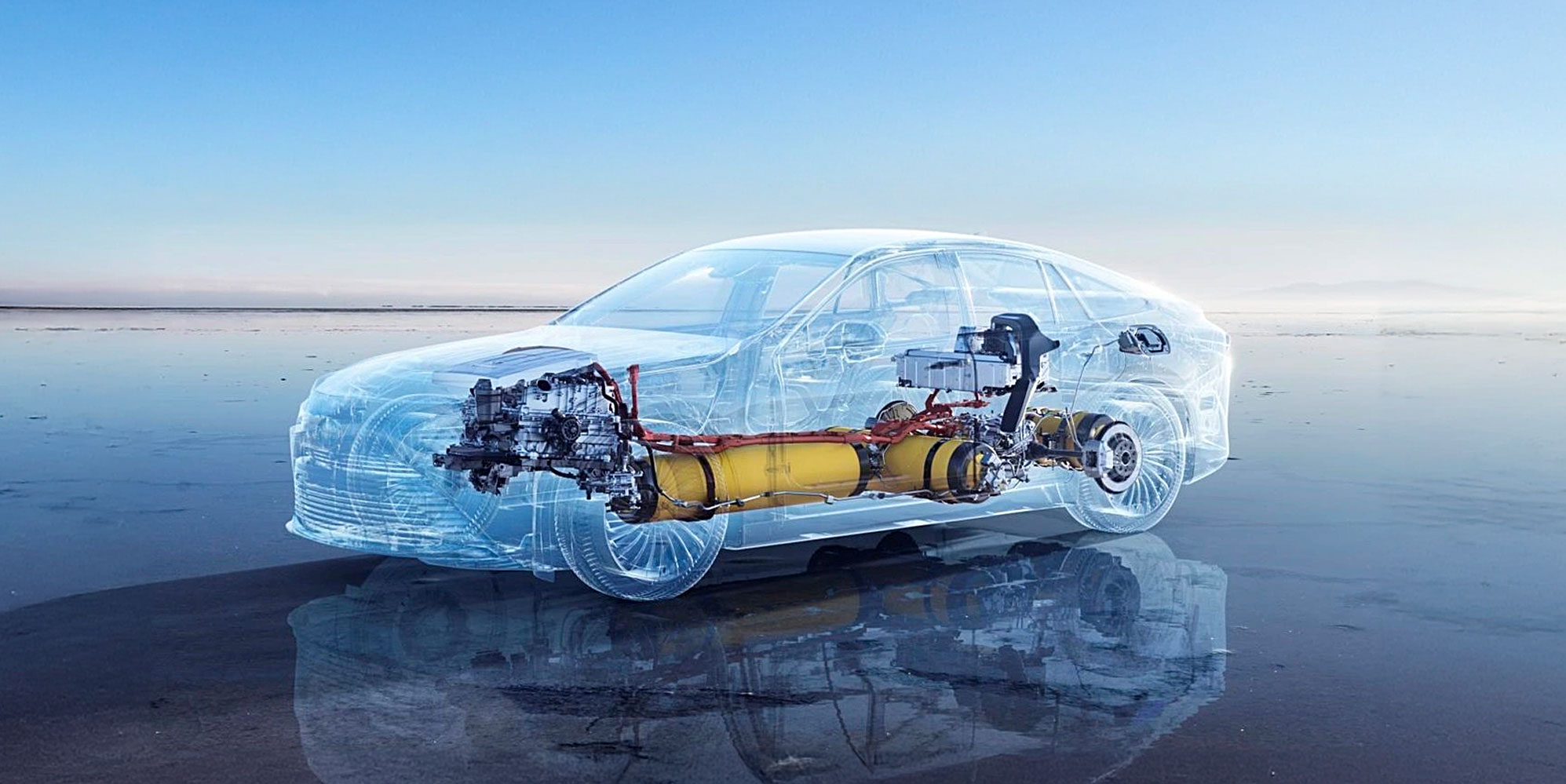
Image source: www.toyota.com.au
As the world looks for cleaner energy solutions, hydrogen fuel cells have emerged as a promising technology to power everything from vehicles to buildings while producing zero emissions. Hydrogen fuel cells combine science, innovation, and sustainability, offering a glimpse into a carbon-free future. But what are hydrogen fuel cells, how do they work, and what are the different types? Let's dive in and explore their potential to revolutionize energy systems.
What is a Hydrogen Fuel Cell?
A hydrogen fuel cell is an energy conversion device that generates electricity, water, and heat through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. Unlike batteries, which store energy, fuel cells generate power as long as fuel (hydrogen) and an oxidant (oxygen) are supplied.
Why It Matters: Hydrogen fuel cells are incredibly clean—the only byproduct is water vapor. This makes them a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels for transportation, power generation, and industrial processes.
How Do Hydrogen Fuel Cells Work?
At its core, a hydrogen fuel cell operates similarly to a battery but without recharge. Here's the step-by-step process:
Hydrogen Input: Hydrogen gas (H₂) is fed into the fuel cell's anode (negative electrode).
Splitting Molecules: At the anode, a catalyst (usually platinum) splits hydrogen into protons (H⁺) and electrons(e⁻).
Electron Flow: The electrons travel through an external circuit, generating an electric current that powers devices or vehicles.
Proton Movement: The protons move through the electrolyte membrane to the cathode (positive electrode).
Reaction at Cathode: At the cathode, electrons, protons, and oxygen (from air) combine to form water (H₂O) and heat.
This process continues as long as hydrogen and oxygen are supplied, creating a continuous source of clean energy.
Key Benefits: Zero emissions (only water vapor). Quiet operation.Scalable for various applications, from cars to power grids.
Types of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Several types of hydrogen fuel cells are designed for specific applications. Here's an overview of the most common types:
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC)
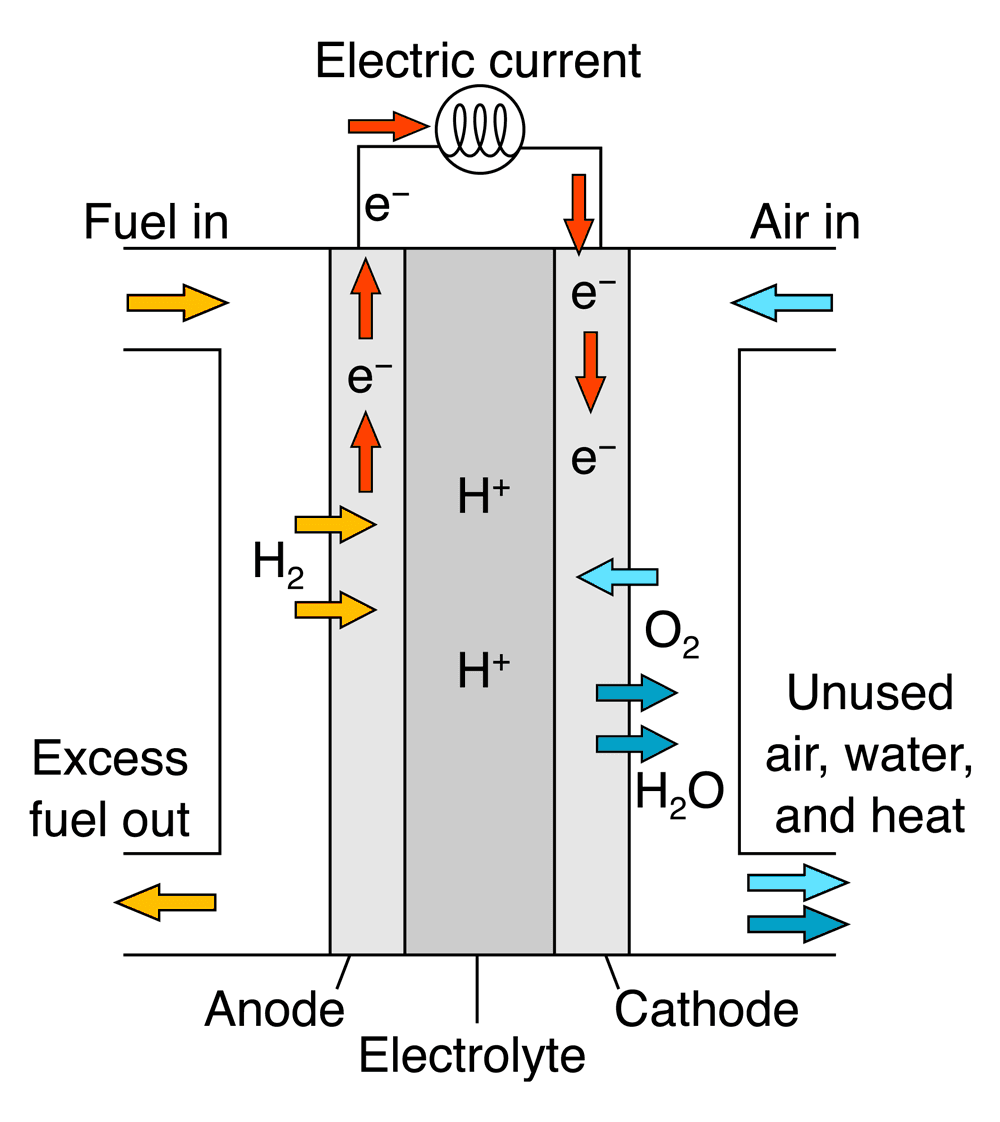
How It Works: A solid polymer electrolyte membrane conducts protons while electrons create an external current.
Applications: Commonly used in cars, buses, trucks, and portable power systems due to their compact size and fast startup.
Advantages: Lightweight, efficient, and suitable for mobile applications.
Example: Toyota's Mirai hydrogen-powered car uses PEM fuel cell technology.
Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC)
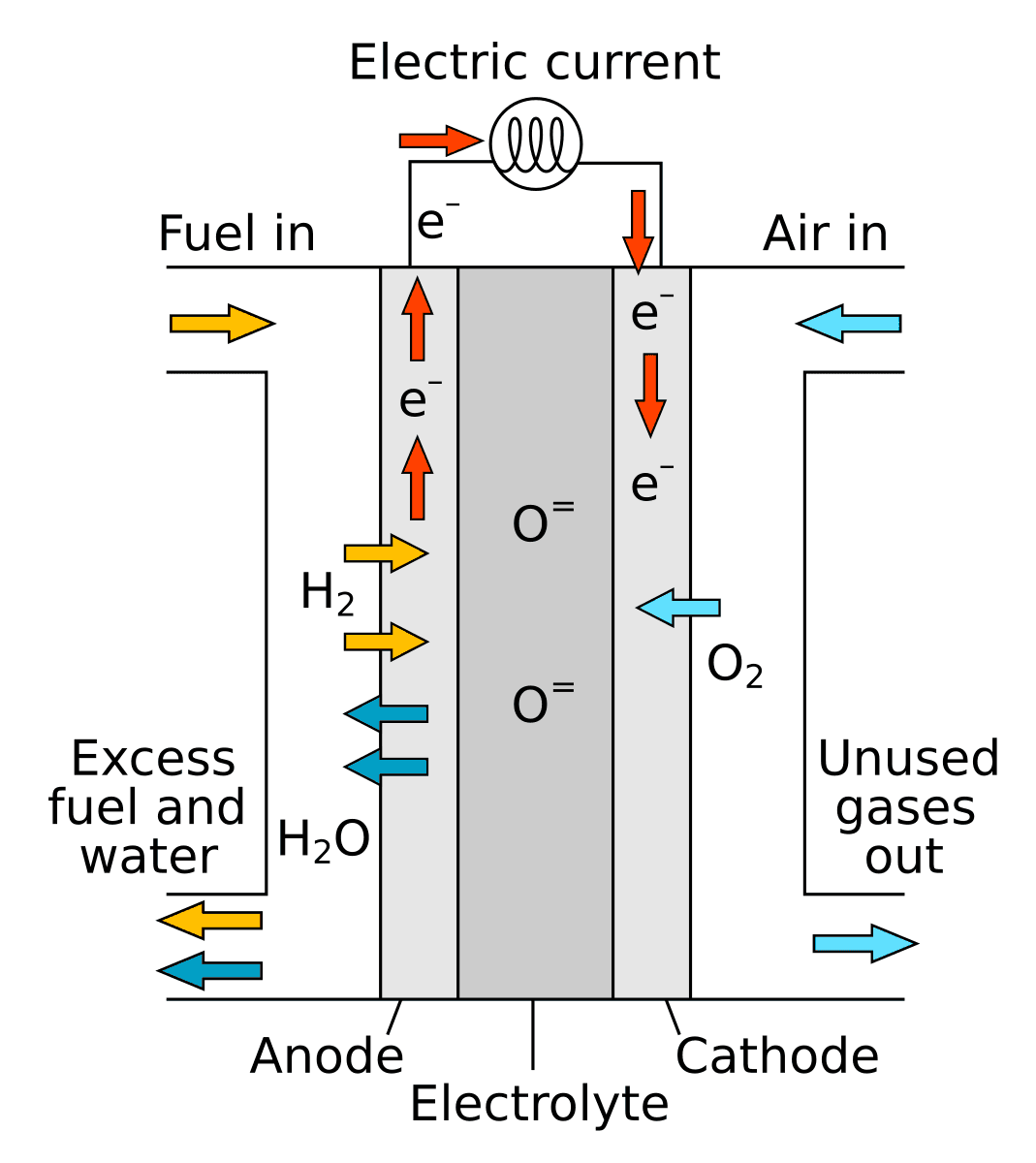
How It Works: A ceramic electrolyte conducts oxygen ions at high temperatures (700–1,000°C).
Applications: Ideal for stationary power generation and industrial applications.
Advantages: It is highly efficient, can use other fuels like methane, and produces heat for combined heat and power (CHP) systems.
Challenges: High operating temperatures require longer startup times and expensive materials.
Alkaline Fuel Cell (AFC)

How It Works: An alkaline electrolyte (potassium hydroxide) conducts hydroxide ions (OH⁻).
Applications: These are used in space missions, including NASA's Apollo and Space Shuttle programs.
Advantages: High efficiency and proven performance.
Challenges: Sensitive to impurities in hydrogen, which limits commercial applications.
Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC)
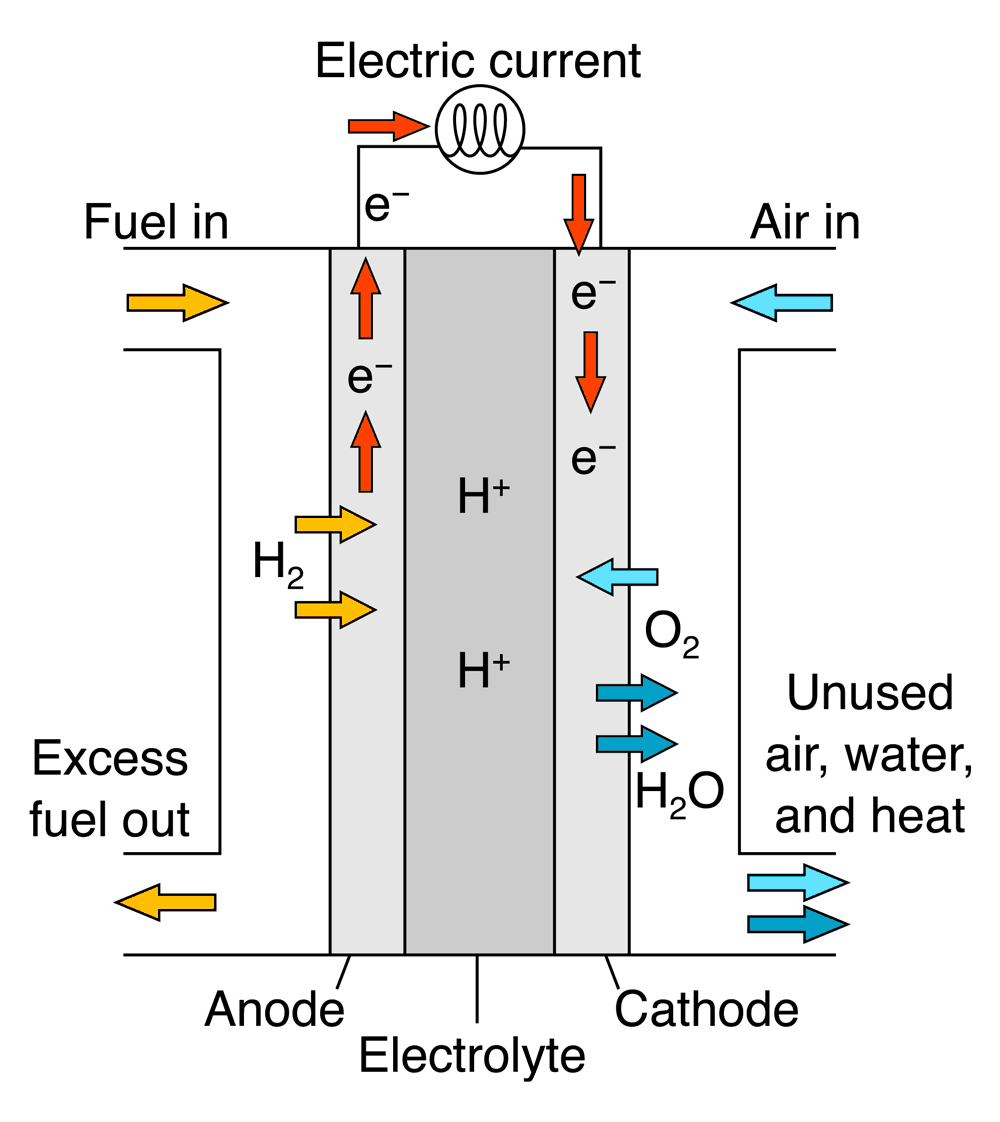
How It Works: Uses liquid phosphoric acid as the electrolyte and operates at medium temperatures (150–200°C).
Applications: Common in stationary power systems for hospitals, buildings, and small-scale energy production.
Advantages: Reliable and can tolerate impure hydrogen.
Challenges: Lower power density than PEMFCs, making it unsuitable for mobile applications.
Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell (MCFC)
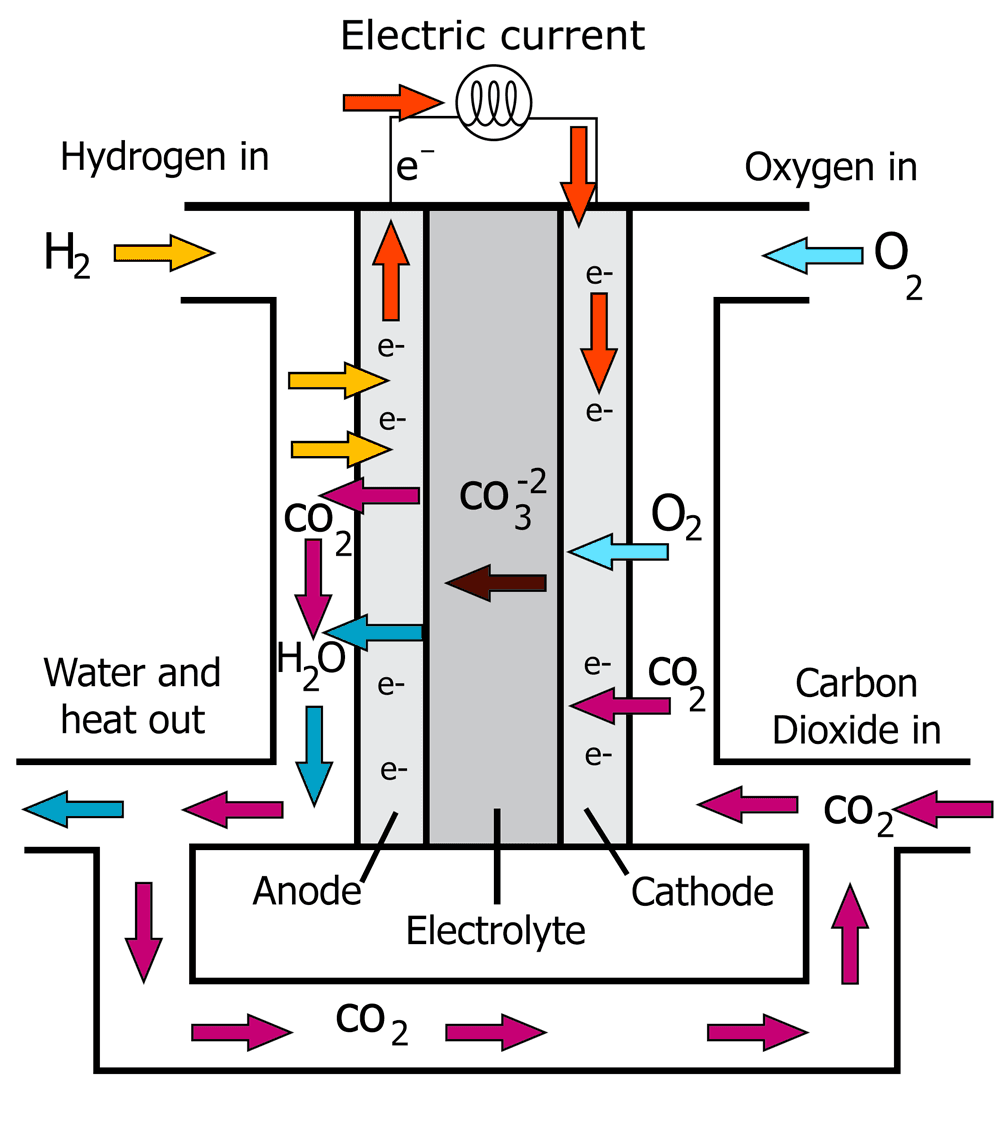
How It Works: Operates at high temperatures (600–700°C) using a molten carbonate salt as the electrolyte.
Applications: Used for large-scale power plants and industrial applications.
Advantages: It is highly efficient, can use hydrogen or natural gas, and produces heat for CHP systems.
Challenges: Requires high operating temperatures and complex maintenance.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A Look Into the Future
As the world pushes for carbon neutrality, hydrogen fuel cells are becoming a key player in sustainable energy systems. Here's what the future looks like:
Decarbonizing Transportation
Hydrogen fuel cells are ideal for heavy-duty vehicles, ships, trains, and even airplanes where batteries are less effective due to weight and range limitations.
Companies like Toyota, Hyundai, and Nikola Motors are scaling up hydrogen fuel cell vehicles for commercial use.
Powering Buildings and Communities
Fuel cells are increasingly used for backup power, heating, and electricity in buildings. Hydrogen microgrids are also being developed to power entire communities with clean energy.
Industrial Applications
Industries like steel manufacturing and chemicals are adopting hydrogen fuel cells to replace fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions.
Renewable Energy Storage
Hydrogen fuel cells will play a critical role in storing excess renewable energy (wind and solar) as hydrogen gas, which can be converted back to electricity when needed.
Space Exploration
Hydrogen fuel cells have been used in space programs since the Apollo missions, providing reliable energy for spacecraft. They will remain essential for powering lunar and Martian bases in future missions.
Global Investments
Governments and private companies heavily invest in green hydrogen production, making hydrogen fuel cells more accessible and cost-effective. Initiatives like Europe's Hydrogen Strategy and the U.S. Hydrogen Shotaim to drive innovation and infrastructure development.
Inspire the Future with the H2GP Foundation
At the H2GP Foundation, we believe in empowering the next generation of hydrogen pioneers. Programs like H2GP XPR, Sprint and H2GP PRO provide students with hands-on experience in hydrogen fuel cell technology, teaching them how to design, build, and innovate clean energy solutions.
By understanding hydrogen's potential, students are equipped to solve real-world challenges and lead the clean energy revolution.
Learn more about hydrogen education and how to get involved at H2GP Foundation.
